A unique new flexible and stretchable device, worn against the skin and capable of producing electrical energy by transforming the compounds present in sweat, was recently developed and patented by CNRS researchers from l »Université Grenoble Alpes and the University of San Diego (U.S.). This cell is already capable of continuously lighting an LED, opening new avenues for the development of wearable electronics powered by autonomous and environmentally friendly biodevices. This research was published in Advanced Functional Materials on September 25, 2019.
This work demonstrates a stretchable and flexible lactate/O2 biofuel cell (BFC) using buckypaper (BP) composed of multi‐walled carbon nanotubes as the electrode material. Free‐standing BP, functionalized with a pyrene‐polynorbornene homopolymer, is fabricated as the immobilization matrix for lactate oxidase (LOx) at the anode and bilirubin oxidase at the cathode. This biofuel cell delivers an open circuit voltage of 0.74 V and a high‐power density of 520 µW cm−2. The functionalized BP electrodes are assembled onto a stretchable screen‐printed current collector with an “island–bridge” configuration, which ensures conformal contact between the wearable BFC and the human body and endows the BFC with excellent performance stability under stretching condition. When applied to the arm of the volunteer, the BFC can generate a maximum power of 450 µW. When connected with a voltage booster, the on‐body BFC is able to power a light emitting diode under both pulse discharge and continuous discharge modes during exercise. This demonstrates the promising potential of the flexible BP‐based BFC as a self‐sustained power source for next‐generation wearable electronics.
Read more @ phys.org
Full paper @ Advanced Functional Materials
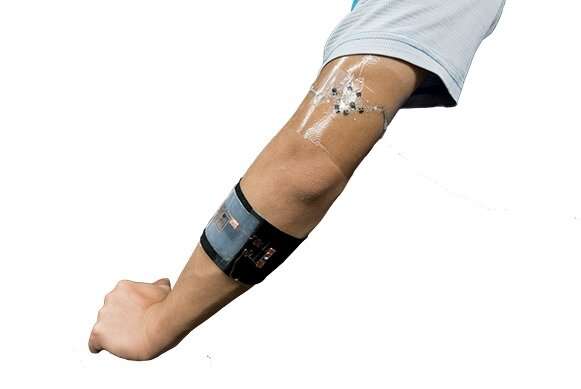
Photo CNRS